This page explains how to set up secure port forwarding through indirect ssh connections.
Contents
Scenario
Let's suppose we connect by ssh from clienthost to hophost, and from there on to targethost, where we want to run a VNC server as securely as possible - which means that only accepts connections from 127.0.0.1 (localhost), not over the network. Let's assume the VNC server uses display :2 and hence listens on port 5902. To connect a client through a secure tunnel, two ssh port forwardings have to be set up:
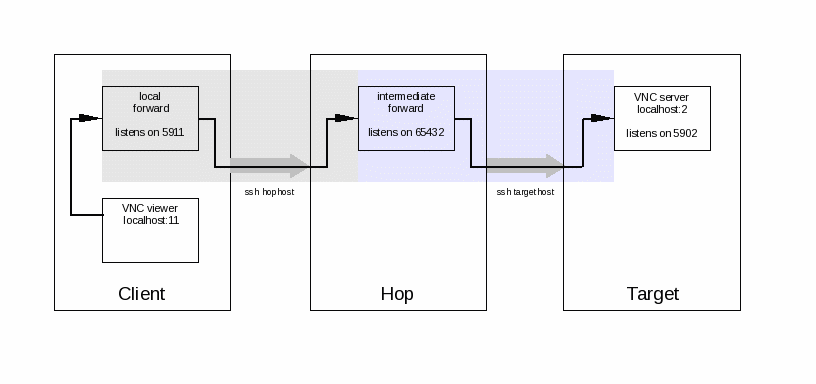
While we could use port 5902 everywhere in this example (provided that it's available on hophost), for clarity we're using port 5911 on the client and port 65432 on the hop host.
It doesn't matter whether the second ssh connection is established automatically (like on a gateway system not allowing actual logins) or manually.
We will now see how to add both required port forwards after the ssh connections have been established:
Step by step
Step 1: establish the ssh connections
'Windows: just connect to hophost as usual (this example will use putty)
Linux: connect as usual, but with a modified escape character:
[clienthost] ~ % ssh -o EscapeChar='^' hophost
If not executed automatically, now connect to the target system:
[hophost] ~ % ssh targethost
In both cases (Windows or Linux client), we can now "escape" both ssh connections independently, and add the port forwards. In the Windows case, the first connection is handled by the putty client, while in the Linux case we use our ^ escape character. In both cases, we use the standard ~ escape to work on the second connection.
Step 2: start the VNC server and determine the target port
[targethost] ~ % vncserver -localhost New 'targethost.domain.de:2 (user)' desktop is targethost.domain.de:2 Starting applications specified in ~user/.vnc/xstartup Log file is ~user/.vnc/targethost.domain.de:2.log
The vncserver script could have chosen a different display number. In this case, modify the port number accordingly (from 5902 to 5900+display) when following the examples.
Step 3: set up the port forward from hop to target host
In the terminal window,
- hit [Enter]
- hit the escape character key [~]
- hit [C]
This will give you a prompt allowing to add the port forward. Only a single command can be entered. ? shows a list.
[targethost] ~ % ssh>
To add the port forward, enter the following command and hit [Enter] twice:
[targethost] ~ % ssh> -L65432:localhost:5902 Forwarding port. [targethost] ~ %
This is just the same option one could have given to the ssh command as well. Now any connection to port 65432 on hophost will effectively connect to port 5902 on targethost.
The choice of port number is arbitrary, within the constraint that users can only use ports > 1023 and that only 64k port numbers exist. If you get an error message channel_setup_fwd_listener: cannot listen to port: 65432, this port is already in use and you have to try another one. There should be plenty of free ports, try numbers above 60000 (but below 65534).
Step 4: set up the port forward from client to hop host
On Linux, the procedure is the same as in the previous step, but now we use the nonstandard escape character we specified for this connection:
- hit [Enter]
- hit [^]
- hit [C]
- specify the required forward:
[targethost] ~ % ssh> -L5911:localhost:65432 Forwarding port. [targethost] ~ %
On Windows, add the forward using the putty GUI. From the window menu, select Change Settings and enter the data:
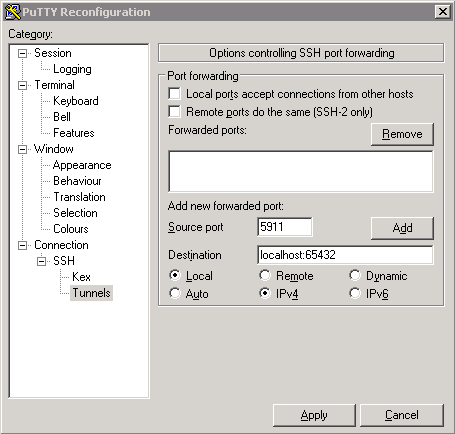
Click Add and then Apply.
Step 5: start the VNC viewer on the client
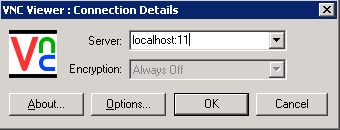
Simply run the command vncviewer localhost:11 . You should be prompted for your VNC password and get access to the server session you started on targethost. Using the Windows GUI, would look like this:
If you want to connect to a different system from the end of the tunnel
Just modify step 3 above. For example, to access an http server on webserver accessible from targethost but not from clienthost and hophost, replace `localhost:5902' by 'webserver:80'.